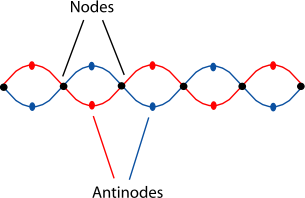
43 draw a standing wave and label the nodes and antinodes
Kristian S. Kuli_Lab Report 6_Phy I.docx - STANDING WAVES... - Course Hero Draw the standing wave and label the Nodes with "N" and Antinodes with "A". 3. Increase the frequency until you find the next one that will establish a standing wave. Find the values listed in Step 2 for this standing wave, enter them into the data table, and draw and label the wave. 4. PDF Chapter 19 Standing Waves Practice Worksheet - Weebly The wavelength of a standing wave can be found by measuring the length of two of the ... b. Label the nodes and antinodes on each of the standing waves shown above. c. How many wavelengths does each standing wave contain? ... a. Draw the standing wave patterns for the first six harmonics. b. Determine the wavelength for each harmonic on the 12 ...
5.05 Lab.docx - Archie Mason Physics 7/9/21 5.05 Lab 1. Use... These will correspond to the first, second, and third overtones. For each standing wave, label the nodes and the antinodes. Label and record the distance in meters of the half wavelength (λ/2) for each standing wave. Explain how the standing wave occurs.
Draw a standing wave and label the nodes and antinodes
Standing Wave Diagrams 1 - Both Ends Fixed - Zona Land Education Below are several static diagrams of standing waves for a medium fixed at both ends, along with the names for each vibration and a count of the antinodes and nodes for each vibration. If you are unclear about the meaning of the terms 'antinode' and 'node', be sure to look back at Understanding Standing Wave Diagrams. Physics Tutorial: Nodes and Anti-nodes - Physics Classroom The nodes and antinodes are labeled on the diagram. When a standing wave pattern is established in a medium, the nodes and the antinodes are always located at the same position along the medium; they are standing still. It is this characteristic that has earned the pattern the name standing wav e. Flickr Physics Photo 16.6 Standing Waves and Resonance - OpenStax The standing wave patterns that are possible for a string, ... nodes at both ends or antinodes at both ends. Example 16.7. Standing Waves on a String Consider a string of L = 2.00 m. ... Draw a sketch of the first three normal modes of the standing waves that can be produced on the string and label each with the wavelength. (c) List the ...
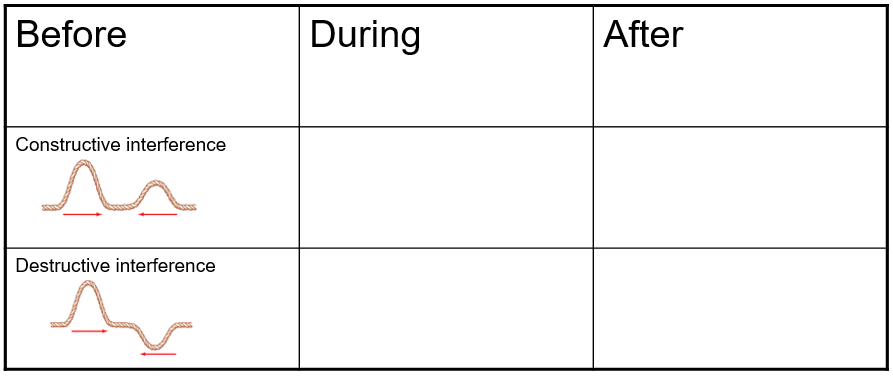
Draw a standing wave and label the nodes and antinodes. Physics Tutorial: Standing Wave Patterns There is an alternating pattern of nodal and antinodal positions in a standing wave pattern. Because the antinodal positions along the guitar string are vibrating back and forth from a large upward displacement to a large downward displacement, the standing wave pattern is often depicted by a diagram such as that shown below. 8386254 (3).docx - Physics | Graded Assignment | Lab... Use the data that you have for the air-filled tube. Make a drawing of the standing wave in the tube when you have two, three, and four nodes or peaks. Standing Waves Lab (3) (Autosaved).docx - Course Hero Part 2 Waves on a string with a fixed end The reflected wave interferes with the original wave and creates a standing wave composed of nodes and antinodes if the frequency is just right. ... Draw and measure the frequencies of the 4 th, 3 rd, 2 nd, ... Draw and label the standing waves for each of the harmonics you discovered: ... Cambridge International AS & A Level Physics Coursebook … Draw the displacement–time graph for the girl from t = 0 to t = 12 s. [1] b On the same graph axes, draw the displacement–time graph for the boy. [2] c Using your graph, determine the value of t when the boy catches up with his sister. [1] [Total: 4] 9 [3] A student drops a small black sphere alongside a vertical scale marked in centimetres.
Physics Tutorial: Harmonics and Patterns This standing wave pattern is characterized by nodes on the two ends of the snakey and an additional node in the exact center of the snakey. As in all standing wave patterns, every node is separated by an antinode. This pattern with three nodes and two antinodes is referred to as the second harmonic and is depicted in the animation shown below. Physics Tutorial: Mathematics of Standing Waves The period is the reciprocal of the frequency. T = 1 / (4.5 Hz) = 0.222 seconds. The wavelength of the wave is related to the length of the rope. For the third harmonic as pictured in this problem, the length of the rope is equivalent to three-halves of a wavelength. That is, L = 1.5 • W where W is the wavelength. PDF Standing Wave Mathematics - BHS Physics Class 4. In each of the two diagrams of standing wave patterns, count the number of nodes and antinodes. 5. Each node is separated by the adjacent node by a distance that is equal to _____ wavelength. 6. Draw the standing wave pattern that would result on the string below if the string vibrated with the first, second, and third harmonic wave patterns. 16.6 Standing Waves and Resonance – University Physics Volume 1 A standing wave is the superposition of two waves which produces a wave that varies in amplitude but does not propagate. Nodes are points of no motion in standing waves. An antinode is the location of maximum amplitude of a standing wave. Normal modes of a wave on a string are the possible standing wave patterns.
Use the data that you have for the air-filled tube. Make a drawing of the standing wave in the tube when you have two, three, and four nodes or peaks. These will correspond to the first, second, and third overtones. For each standing wave, label the nodes and the antinodes. Label and record the distance in meters of the half wavelength (λ/2) for each standing wave. PDF Standing Waves - Fulmer's Physics Label the nodes and antinodes on each of the standing waves shown below. c. How many wavelengths does each standing wave contain? d. Determine the wavelength of each standing wave. ... Draw the standing wave patterns for the first six harmonics. b. Determine the wavelength for each harmonic on the 12 meter rope. Record the values in the table ... Standing Wave Diagrams 3 - One Fixed End and One Open End | Zona Land ... Below are several static diagrams of standing waves for a medium fixed at end and open at the other, along with the names for each vibration and a count of the antinodes and nodes for each vibration. If you are unclear about the meaning of the terms 'antinode' and 'node', be sure to look back at Understanding Standing Wave Diagrams. ELECTRONICS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM BY GEORGE KENNEDY… Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Wave Phenomena - StickMan Physics Standing Wave Nodes and Antinodes. Standing waves max amplitude areas are called antinodes. The picture has 4 antinodes. The areas of complete destructive interference are called nodes. Nodes are areas where a rope appears not to move. ... Draw and label (node and antinode) of a standing wave with 3 nodes and 2 antinodes;
Wave Phenomena - StickMan Physics Standing Wave. A standing wave is created by a wave and its reflection but only at frequencies where each end of a rope has a node. Standing waves have the same frequency, wavelength, and amplitude traveling in opposite directions and interfering. consists of nodes (amplitude) and antinodes (max amplitude)
What is node and anti node? - UrbanPro.com In a sense, these points are the opposite of nodes, and so they are called antinodes. A standing wave pattern always consists of an alternating pattern of nodes and antinodes. The animation shown below depicts a rope vibrating with a standing wave pattern. The nodes and antinodes are labeled on the diagram.
Solved Draw the standing wave patterns described below. | Chegg.com Science Physics Physics questions and answers Draw the standing wave patterns described below. Label both the nodes and the anti-nodes. a) The 3rd harmonic of a string b) The 4th harmonic of an air column open at both ends c) The 5h harmonic of an air column that is opened at one only. Question: Draw the standing wave patterns described below.
How do you calculate the wavelength of a standing wave? If you know the distance between nodes and antinodes then use this equation: λ 2 = D. Where D is the distance between adjacent nodes or antinodes. If you know the harmonic and length of string then you need to relate the wavelength to the length of string/pipe (L) using the following: For strings and open pipes. Harmonic, Wavelength in terms of L.
PDF Key Vocabulary: Wave Interference Standing Wave Node Antinode ... - Weebly This standing wave pattern is characterized by nodes on the two ends of the slinky and an additional node in the exact center of the slinky. As in all standing wave patterns, every node is separated by an antinode. This pattern with three nodesand two antinodesis referred to as the second harmonicand is depicted in the picture shown below.
Standing Waves - The Physics Hypertextbook A node will always form at the fixed end while an antinode will always form at the free end. The simplest standing wave that can form under these circumstances is one-quarter wavelength long. To make the next possible standing wave add both a node and an antinode, dividing the drawing up into thirds. We now have three-quarters of a wavelength.
5.05 lab.docx - Physics | Graded Assignment | Lab Report:... Use the data that you have for the air-filled tube. Make a drawing of the standing wave in the tube when you have two, three, and four nodes or peaks. These will correspond to the first, second, and third overtones. For each standing wave, label the nodes and the antinodes. Label and record the distance in meters of the half wavelength (λ/2 ...



Post a Comment for "43 draw a standing wave and label the nodes and antinodes"